This article provides a comprehensive guide to RTVI AI, also known as Real-Time Voice Interaction AI, a protocol designed to enhance the development of real-time voice and multimodal applications. It begins with an introduction to RTVI AI, explaining how it standardizes communication between client applications and server-side services to facilitate seamless voice and text interactions. The article then delves into how RTVI AI operates, highlighting the specialized processors that manage tasks such as transcription and text-to-speech conversion, which are crucial for real-time communication. The architecture of RTVI AI is explored next, detailing its structure and how it supports various real-time AI use cases through standardized events and configurable services. Readers will also learn about the specific events and services within RTVI AI, which allow for flexible and customizable application development. Finally, the article provides a step-by-step guide on building a simple RTVI AI application using Python, offering an explanation of the code to help developers understand how to implement and manage real-time voice interactions effectively. This guide is designed to be accessible to both technical and non-technical readers, providing clear insights into the workings and applications of RTVI AI.
Introduction to RTVI AI
RTVI AI, or Real-Time Voice Interaction AI, is a cutting-edge protocol designed to streamline the development of real-time voice and multimodal applications. This protocol establishes a standardized communication framework between client-side applications and server-side inference services. By doing so, it enables seamless integration and efficient processing of voice, text, and other multimodal interactions.
The design of RTVI AI focuses on facilitating natural turn-taking, transcription, and response generation. This is achieved through a series of specialized processors that manage different aspects of communication, such as speaking states and transcription. These processors work in a pipeline, converting internal data frames into standardized messages that clients can easily interpret and act upon.
One of the key strengths of RTVI AI is its flexibility and adaptability, which allow it to support a wide range of real-time AI use cases. Whether it’s handling voice-to-voice inference loops, generating real-time video content, or orchestrating multiple AI models, RTVI AI provides a robust framework for building sophisticated applications. This makes it an ideal choice for developers looking to create advanced AI-driven solutions in sectors like healthcare, customer service, and education.
By leveraging the power of RTVI AI, developers can build applications that not only process speech and generate responses efficiently but also offer a seamless user experience through natural and intuitive interactions.
How RTVI AI Works
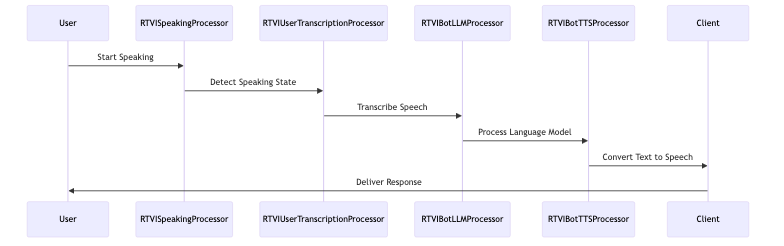
RTVI AI operates using a sophisticated pipeline of specialized processors that work in tandem to convert internal Pipecat frames into standardized messages. These messages are understood by clients, allowing for seamless communication and interaction. Each processor within the pipeline is tasked with handling a specific aspect of voice interaction, ensuring that data is processed efficiently and interactions are managed effectively.
Key Processors in the Pipeline
- Speaking State Management:
- The RTVISpeakingProcessor is responsible for managing speaking state changes. It tracks when users and bots start or stop speaking, facilitating natural turn-taking and reducing interruptions during conversations.
- Real-Time Transcription:
- The RTVIUserTranscriptionProcessor handles the real-time conversion of spoken words into text. This processor ensures that user speech is transcribed accurately and promptly, providing immediate feedback that is crucial for interactive applications.
- Language Model Processing:
- The RTVIBotLLMProcessor manages language model (LLM) responses. It processes the text generated by language models and converts it into a format that can be easily interpreted by the client, allowing for dynamic and contextually relevant interactions.
- Text-to-Speech Conversion:
- The RTVIBotTTSProcessor oversees the text-to-speech (TTS) conversion process. It transforms textual responses into spoken words, ensuring that the bot’s responses are delivered audibly and naturally to the user.
Data Flow and Interaction Management
The data flow within RTVI AI begins with the input received from the transport layer. This input is processed through each stage of the pipeline, where each processor performs its designated task. For instance, the speaking state processor will first determine if a user or bot is speaking, followed by transcription of the speech, processing by the language model, and finally, conversion into speech for output.
This structured approach to data processing ensures that each interaction is handled with precision, allowing for real-time feedback and communication. The pipeline’s design is inherently modular, meaning that it can be adapted and extended to suit various application requirements. This makes RTVI AI highly suitable for applications that demand low-latency processing and immediate interaction, such as customer service bots, virtual assistants, and interactive voice response systems.
Architecture of RTVI AI
The architecture of RTVI AI is ingeniously designed to facilitate seamless communication and interaction between inference servers and clients. At its core, it is built around a set of abstractions and message formats that standardize the communication process. This ensures that both audio and video streams, as well as session states, metrics, and errors, are managed efficiently and consistently.
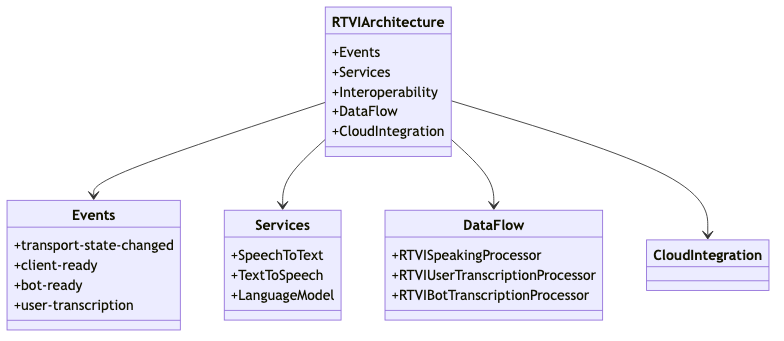
Key Components of the Architecture
-
Events: The architecture defines a concise set of events that are essential for managing the lifecycle of audio and video streams. These events include state changes, session management, and error notifications. Examples of such events are
transport-state-changed,client-ready,bot-ready, anduser-transcription. -
Services: A standout feature of RTVI AI is its generic services mechanism. Inference servers expose configurable services that clients can interact with. These services typically include speech-to-text (STT), text-to-speech (TTS), and language model (LLM) processing. This modular approach allows for flexibility in how services are configured and executed, making it possible to tailor the system to specific use cases.
-
Interoperability and Adaptability: The architecture promotes interoperability by defining client-side constraints while allowing server-side architectures to remain flexible. This means that different models and services can be integrated and orchestrated in real-time without being restricted by client-side implementations. This adaptability makes RTVI AI suitable for a wide range of real-time AI applications, from simple voice-to-voice interactions to complex multimodal communication systems.
Data Flow and Processing
Data flow within RTVI AI is managed through a pipeline of specialized processors. Each processor is responsible for a specific aspect of the conversation, such as managing speaking states, transcription, and language model processing. The data flow begins with input from the transport layer, which is then processed by various RTVI processors like RTVISpeakingProcessor for speaking state, RTVIUserTranscriptionProcessor for user speech transcription, and RTVIBotTranscriptionProcessor for bot speech transcription. This sequential processing ensures that data is handled efficiently from input to output, ultimately being transmitted back to the client through the transport layer.
Cloud Integration
Cloud computing plays a pivotal role in the architecture by providing the necessary scalability and flexibility. It allows for the integration and orchestration of different models and services in real-time, supporting cross-platform development across Web, iOS, Android, Linux, macOS, and Windows. The cloud infrastructure ensures that the system can handle increased data loads and user demands efficiently, leveraging techniques like load balancing and autoscaling.
By focusing on these architectural elements, RTVI AI delivers a robust framework for developing sophisticated real-time voice and video applications, ensuring low latency, high interoperability, and adaptability across various platforms and use cases.
Events and Services in RTVI AI
In the architecture of RTVI AI, events and services play a pivotal role in managing real-time interactions. The protocol defines a series of standard event messages that enable seamless communication between clients and servers. These events include:
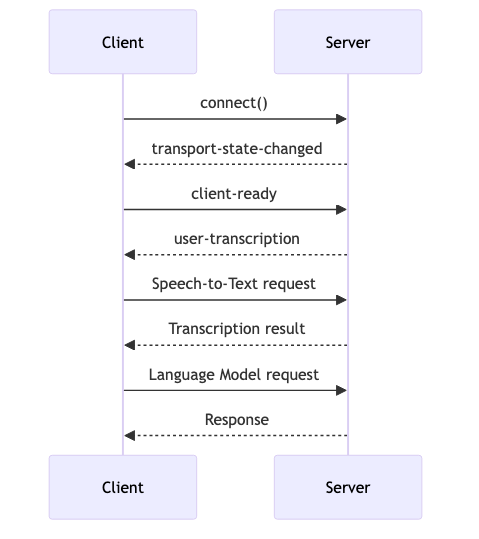
-
transport-state-changed: This event is triggered when there is a change in the state of the transport layer, such as connecting or disconnecting from the server. It ensures that clients are aware of the current connection status and can respond accordingly. -
client-ready: This event signals that the client is prepared to initiate interaction with the server. It is crucial for synchronizing the start of sessions and ensuring that the server is ready to handle incoming data. -
user-transcription: This event handles real-time transcription of user speech, providing immediate text output that can be processed by the system. It is essential for applications that require speech-to-text capabilities, allowing for dynamic and responsive user interactions.
In addition to events, RTVI AI offers a range of services that are designed to be flexible and customizable. These services include:
-
Speech-to-Text (STT): This service converts spoken language into written text, enabling applications to process and respond to user speech in real-time. It can be configured to use different models and parameters based on the specific needs of the application.
-
Language Model (LLM): This service manages the processing of language inputs and generates contextually relevant responses. Developers can specify particular models and adjust settings to optimize performance for their use cases.
These services are abstract containers for configuration and actions, allowing developers to define unique functionalities and adjust parameters to meet specific application requirements. By providing a standardized interface for service configuration, RTVI AI simplifies the integration and management of complex AI-driven functionalities, supporting a wide range of real-time multimedia applications.
Building a Simple RTVI AI Using Python
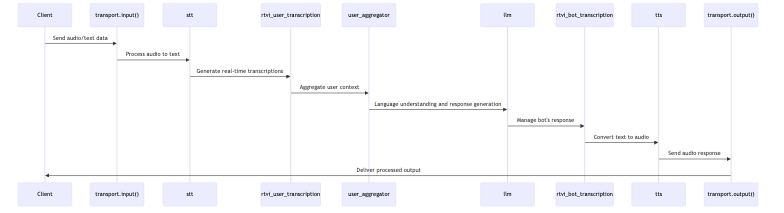
Creating a simple RTVI AI application using Python involves leveraging the Pipecat library’s processors to manage various aspects of real-time voice interaction. The core component of this setup is the RTVIProcessor, which orchestrates communication between the client and the server, handling speaking states, user transcription, and language model responses.
Setting Up the Environment
Before diving into the code, ensure that you have the Pipecat library installed in your Python environment. If you haven’t installed it yet, you can typically do so using pip:
pip install pipecat
Implementing the Pipeline
The following code snippet demonstrates how to set up a basic pipeline using the Pipecat library. This pipeline will handle speaking state changes, transcribe user speech, and manage language model responses:
from pipecat.processors.rtvi import (
RTVIProcessor,
RTVISpeakingProcessor,
RTVIUserTranscriptionProcessor,
RTVIBotTranscriptionProcessor,
RTVIBotLLMProcessor,
RTVIBotTTSProcessor
)
# Create processors
rtvi_speaking = RTVISpeakingProcessor() # Manages speaking state changes
rtvi_user_transcription = RTVIUserTranscriptionProcessor() # Handles user speech transcription
rtvi_bot_transcription = RTVIBotTranscriptionProcessor() # Manages bot speech transcription
# Chain them together in a pipeline
processors = [
transport.input(),
rtvi_speaking,
stt, # Speech-to-text processor
rtvi_user_transcription, # User transcription processor
user_aggregator, # User context aggregation
llm, # Language model processor
rtvi_bot_transcription, # Bot transcription processor
tts, # Text-to-speech processor
transport.output()
]
pipeline = Pipeline(processors)
# Start the bot
await rtvi.set_bot_ready()
Explanation of the Code
- RTVIProcessor: This is the main coordinator that manages client communication, service configuration, and action execution.
- RTVISpeakingProcessor: Tracks when users and bots are speaking, ensuring accurate turn-taking.
- RTVIUserTranscriptionProcessor: Converts user speech to text in real-time, providing immediate feedback.
- RTVIBotTranscriptionProcessor: Aggregates bot responses and manages their transcription.
- Pipeline: Chains together the processors to handle different aspects of the interaction, from input to output.
By chaining these processors in a pipeline, you can efficiently manage the flow of data between clients and servers, allowing for real-time processing of voice interactions. This modular approach exemplifies the flexibility and scalability of RTVI AI, making it suitable for a wide range of applications that require dynamic and responsive voice interaction capabilities.



