This article is a comprehensive guide for Python developers looking to enhance their project management and development workflow using Git versioning, Continuous Integration (CI), and GitHub Actions. It begins by explaining the fundamental role of Git in tracking changes and facilitating collaboration in software projects. Next, it provides a step-by-step guide on setting up Git for a Python project, ensuring a smooth workflow by covering essential practices like initializing repositories and managing unnecessary files. The article then introduces Continuous Integration, highlighting its benefits such as early bug detection and improved software quality. Following this, it delves into implementing GitHub Actions to automate tasks like testing and deployment, offering clear instructions to streamline the CI process. Additionally, the article shares best practices for combining Git versioning with CI and GitHub Actions to maintain efficiency and project integrity. Finally, it concludes by summarizing the key points and offering resources for further learning, emphasizing the importance of mastering these tools to stay competitive in software development.
Introduction to Git Versioning
Version control is the backbone of modern software development, and Git is one of the most popular systems used by developers worldwide. In this section, we will explore the importance of versioning in software projects, particularly in Python. We’ll discuss how Git helps track changes, manage collaboration, and maintain a history of project development. Understanding the fundamentals of Git versioning is crucial for efficient project management and successful collaboration among team members.
Why Version Control Matters
In any development project, the ability to track changes over time is essential. Git enables developers to:
- Track Changes: Every modification in the codebase is recorded, allowing developers to revert to previous versions if needed.
- Facilitate Collaboration: Multiple developers can work on the same project simultaneously without overwriting each other’s work, thanks to branching and merging.
- Preserve History: Git maintains a detailed history of changes, which is invaluable for understanding the evolution of a project and debugging.
Setting Up Git for Your Python Project
Before diving into version control, it’s important to configure Git with your user information:
git config --global user.name "Your Name"
git config --global user.email "your.email@example.com"
This setup ensures that your identity is associated with your commits, providing accurate attribution and history tracking.
Key Concepts in Git Versioning
Branching and Merging
Branching allows developers to work on different features or fixes concurrently. Once a branch is complete, it can be merged back into the main branch. This process supports parallel development and feature isolation.
Handling Merge Conflicts
Conflicts can arise when changes in different branches affect the same lines of code. Git highlights these conflicts, and developers must manually resolve them by editing the conflicting files.
Rebasing
Rebasing re-applies commits on top of another branch, creating a linear project history. While it can streamline the commit history, it should be used cautiously, especially in shared branches.
Managing Remote Repositories
GitHub and other platforms host remote repositories, enabling collaboration across teams. Managing remotes involves adding, removing, and syncing repositories:
git remote add origin <url>
This command connects your local repository to a remote one, facilitating collaboration and code sharing.
Utilizing Git Hooks
Git hooks are scripts that run automatically at specific points in the Git lifecycle. They can automate tasks like running tests or enforcing commit message standards, enhancing workflow efficiency.
By mastering these concepts, you can leverage Git to its full potential, ensuring a robust and organized development process for your Python projects.
Setting Up Git for Your Python Project

Before diving into continuous integration and GitHub Actions, it’s essential to set up Git correctly for your Python project. This section will guide you through initializing a Git repository, creating a .gitignore file to manage unnecessary files, and setting up branch strategies. We’ll also cover best practices for committing code, writing meaningful commit messages, and using tags to mark release points in your project. Proper setup ensures a smooth workflow and prepares your project for CI integration.
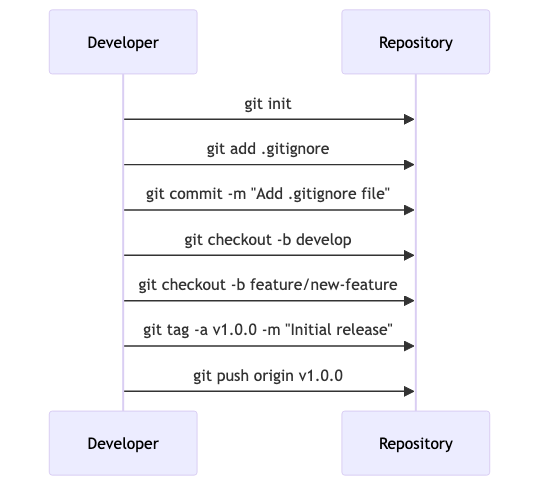
Initializing a Git Repository
To start, navigate to your project directory in the terminal and initialize a Git repository:
git init
This command creates a new .git directory in your project, where Git stores all its versioning data.
Creating a .gitignore File
The .gitignore file is crucial for excluding files that are not necessary for version control, such as temporary files, logs, and environment configurations. Here’s a basic example for a Python project:
__pycache__/
*.pyc
.env
*.log
Add this file to your repository to keep your commits clean:
git add .gitignore
git commit -m "Add .gitignore file"
Setting Up Branch Strategies
A well-defined branch strategy helps manage features, fixes, and releases efficiently. Consider using the following branches:
- main: The stable version of your project.
- develop: The integration branch for features and fixes.
- feature/xyz: Branches for individual features or enhancements.
Create branches using:
git checkout -b develop
git checkout -b feature/new-feature
Best Practices for Committing Code
- Commit Often: Make small, frequent commits to keep track of changes.
- Write Meaningful Messages: Start with a short summary, followed by a detailed description if necessary.
Example commit message:
Add user authentication feature
- Implement login and signup functionality
- Add JWT for secure sessions
Using Tags to Mark Release Points
Tags are useful for marking significant points in your project’s history, like releases. To create a tag:
git tag -a v1.0.0 -m "Initial release"
git push origin v1.0.0
This practice helps in tracking versions and rolling back changes if needed.
With these foundational steps, your Python project will be well-organized and ready for continuous integration and further automation with GitHub Actions.
Introduction to Continuous Integration (CI)

Continuous Integration (CI) is a cornerstone of modern software development, particularly in Python projects, where agility and rapid iteration are key. CI is a practice where developers frequently integrate their code changes into a shared repository. This approach allows teams to detect and address bugs early, improving software quality and accelerating release cycles.
Benefits of CI
Early Bug Detection
By integrating code frequently, CI enables developers to identify errors early in the development process. Automated testing runs with each integration, catching issues before they escalate. This proactive bug detection reduces the time spent on debugging later stages.
Improved Software Quality
CI promotes a culture of continuous testing and validation. With each code change, a suite of automated tests ensures that new features don’t break existing functionality. This continuous feedback loop enhances the overall quality and reliability of the software.
Faster Release Cycles
CI streamlines the development workflow, allowing teams to release updates more frequently. Automated builds and tests mean that code is always in a deployable state, reducing the time between development and deployment.
CI in the Development Workflow
Incorporating CI into your development workflow involves several key steps:
-
Version Control: Use a version control system like Git to manage code changes. CI relies on a central repository where code is regularly pushed and integrated.
-
Automated Testing: Implement a robust suite of automated tests. These tests run with every code integration, ensuring that new changes don’t introduce regressions.
-
Build Automation: Automate the build process to compile and package your application. This reduces human error and ensures consistency across environments.
-
Feedback and Monitoring: Utilize CI tools to provide immediate feedback to developers. Monitoring integration results helps maintain code quality and stability.
Why CI is Beneficial for Python Projects
Python’s dynamic nature and extensive libraries make it ideal for rapid development. However, this flexibility can lead to integration challenges. CI mitigates these issues by:
- Ensuring Compatibility: Automated tests verify that code changes are compatible with existing codebases and libraries.
- Facilitating Collaboration: CI allows multiple developers to work on the same project without conflicts, as integrations are frequent and systematic.
- Enhancing Efficiency: With CI, Python projects benefit from automated processes that handle repetitive tasks, freeing developers to focus on feature development.
Understanding and implementing CI in your Python projects will not only enhance your development efficiency but also improve the quality and reliability of your software. In the next sections, we’ll explore specific tools and practices to help you set up a robust CI pipeline tailored to your needs.
Implementing GitHub Actions for CI
GitHub Actions is a powerful tool for automating workflows directly within your GitHub repository. In this section, we’ll explore how to set up GitHub Actions to automate testing, building, and deploying your Python project. By the end of this section, you’ll be equipped to leverage GitHub Actions to enhance your development pipeline.
Setting Up Your First Workflow
To begin, create a new directory in your repository named .github/workflows. Inside, add a YAML file, such as ci.yml, to define your workflow.
Here’s a basic example to get you started:
name: CI
on: [ push, pull_request ]
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Set up Python
uses: actions/setup-python@v2
with:
python-version: '3.8'
- name: Install dependencies
run: |
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
pip install -r requirements.txt
- name: Run tests
run: |
pytest
Configuring Triggers
Triggers determine when your workflows run. In the example above, the workflow triggers on push and pull_request events. You can customize these triggers to suit your needs:
-
Push to Specific Branches:
on: push: branches: - main - develop -
Scheduled Workflows:
on: schedule: - cron: '0 0 * * *' # Runs every day at midnight
Using Pre-built Actions
GitHub Actions offers a plethora of pre-built actions to streamline your CI process. For instance, actions/checkout checks out your repository, and actions/setup-python sets up the Python environment.
You can explore more actions in the GitHub Marketplace.
Leveraging Matrix Builds
Matrix builds allow you to test across multiple environments. Here’s how you can define a matrix strategy to test different Python versions:
strategy:
matrix:
python-version: [ 3.6, 3.7, 3.8, 3.9 ]
This configuration will run your tests across all specified Python versions, ensuring compatibility.
Managing Secrets
Securely manage sensitive information using GitHub Secrets. Add secrets in your repository settings and access them in your workflow using the secrets context:
env:
MY_SECRET_KEY: $
Caching Dependencies
Improve build times by caching dependencies. Use the actions/cache action to cache your pip dependencies:
- name: Cache pip
uses: actions/cache@v2
with:
path: ~/.cache/pip
key: ${{ runner.os }}-pip-${{ hashFiles('**/requirements.txt') }}
restore-keys: |
${{ runner.os }}-pip-
By implementing these practices, you can create a robust CI pipeline that automates testing, building, and deployment for your Python projects.
Best Practices for Versioning with CI and GitHub Actions
Combining Git versioning with CI and GitHub Actions requires following best practices to maximize efficiency and maintain project integrity. This section will cover strategies for effective branching, version tagging, and automated testing. We’ll also discuss handling merge conflicts and ensuring code quality through automated checks.
Effective Branching Strategy
A well-defined branching strategy is crucial for managing version control in a collaborative environment. Here’s a common approach:
- Main Branch: This branch should always be in a deployable state. It contains the latest stable release.
- Develop Branch: Used for integrating features before they’re ready for the main branch.
- Feature Branches: Created for working on new features or bug fixes. These branches are short-lived and merged back into the develop branch.
Version Tagging with GitHub Actions
Automating version tagging can streamline your release process. Use GitHub Actions to tag versions based on commit messages or other criteria:
name: Tag Version
on:
push:
branches:
- main
jobs:
tag:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Set up Git
run: |
git config user.name "GitHub Action"
git config user.email "action@github.com"
- name: Tag Version
run: |
git tag v1.0.0
git push origin v1.0.0
Automated Testing and Code Quality
Automated testing ensures code quality and reliability:
- Unit Tests: Run unit tests on every push to detect issues early.
- Code Coverage: Integrate tools like Codecov to monitor test coverage.
- Linting: Use linters to maintain code style and quality.
Handling Merge Conflicts
Merge conflicts are inevitable in collaborative projects. Here are some advanced strategies:
- Rebase Regularly: Keep feature branches updated with the latest changes from the develop branch to minimize conflicts.
- Conflict Resolution Tools: Use tools like
git mergetoolor IDE-integrated conflict resolvers for complex conflicts.
Ensuring Security in Workflows
Security best practices in GitHub Actions include:
- Secrets Management: Use GitHub Secrets to store sensitive information securely.
- Permissions: Limit workflow permissions to only what’s necessary.
Continuous Improvement
Regularly review and refine your CI/CD processes to adapt to changing requirements and improve efficiency. Encourage team feedback and stay informed about new tools and practices.
By adhering to these best practices, you’ll ensure a robust and reliable development process that minimizes errors and accelerates delivery.




